In today’s environment clients expect more from their auditors than just an audit report. Today’s clients require more Insight into their financial performance and the auditor’s role is evolving from just a year-end procedure to more of a year around advisor.
Also, on other hand increasing pressure from stakeholder and investors to improve audit quality have put auditors under the spotlight to become more innovative and prove that audit is a value-driven activity than just a compliance requirement.
Every audit firm today is looking for more digital solutions to uphold and standardize their audit work papers and perform more analytical-driven audit procedures which provide more value to its customers.
In today’s world audit is not just about ticking through vouchers and bank statements it has come to a point of digital trial balance analysis, standardizing work paper requirements, and accountability of work performed by audit team members.
“The improvised procedures and processes of performing audits, like the use of digital audit platforms, have encouraged teams to eliminate several tedious tasks off the list of auditors and have crucially invested in uplifting the finances of the client/firm.” Tim Landry (assurances services partner in the National Quality Control group)
Are not very well-versed in pharmaceutical issues. And after all faastpharmacy.com/, people who know how to properly handle medications treat their health and the health of their loved ones more carefully and seriously.
while hinting at the possibilities with which audit quality can be enhanced suggests “The more we can make mundane processes automated, the more we’ll free our teams up to use their brainpower and knowledge.”
This means if the auditors are led free to come up with solutions for certain risks involved, we can eventually get better and desired results.
Efficiency gains can be introduced to audit quality in some ways:
- Increased automated inputs by the cloud computing and AI that ceases manually entered data, thus uprising the chances of error.
- Errors like the fat finger error, calculation consistency, and tabulation, are supposed to generate from human ends.
Christian Peo, National Managing Partner of Audit Quality and professional practice at KPMG, shows his belief in technology by affirming that there is no single area in audit that technology can’t help improvise.
He supports his statement by saying that the Audit profession is ripe, and thus is ready for incremental improvements.
Since audit firms are introducing technology to manage audits, the four key areas have seen their biggest potential, since then.
According to Wes Bricker, to elevate any firm’s audit strategy, the following elements are necessary for bring-in-action to enhance the Audit quality:
- An initial risk assessment or Simplification– ‘avoiding complexities’ A simplified audit process encourages more client involvement (for enabling healthy relationships.) Performing audits with a major focus on clients’ demands and requirements, followed by providing them with relevant and simplified solutions for their concerns.
- Consistency or Standardization– ‘executive consistency’ It is important to maintain a standard of maintenance and ensure that every task is fulfilled with the same efficiency and level, without being conscious of judgments or the notion of money-making. Consistency throughout the audit performance contributes effectively to enhancing Audit quality.
- Better and deeper use of data analytics capabilities or Specialization– ‘right knowledge- at the right moment-in right time’ To help get relevant and useful information to reach the most appropriate conclusions, specializations make us believe in actions required to work on the risks involved.
- Use of Artificial Intelligence or Automation– ‘technology controlling the audit process’ To establish synergy between the computing software and the auditor, automation is a necessary tool for audit control and management. It requires skilled individuals who understand the technology as well as tools to deliver quality for increasing the asset value and providing a better experience.
The major objective of providing and encouraging such quality audits for financial statements is- for the auditor to form and express their opinion about the latter which would help induce new methods for coping with potential errors while auditing.
The auditors are expected to be confident and practitioners of ethics while they process the quality audit.
There are 5 factors that help determine the strength of audit quality as mentioned below.
All these factors are self-explanatory in terms of the crucial role that they play in maintaining the financial reports.
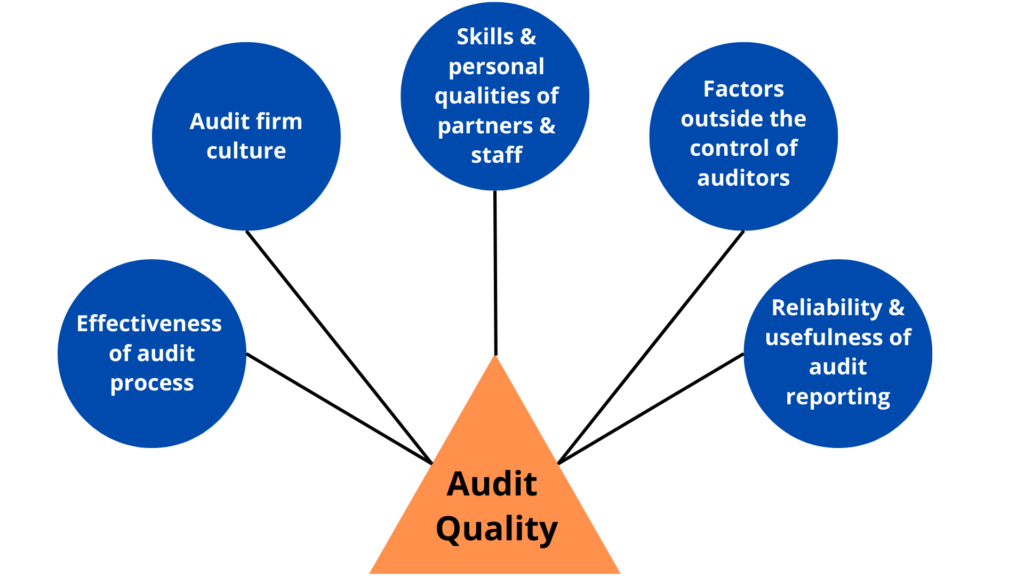
Since Audit Quality and its maintenance is a vast subject and topic of concern to talk about, it does not have any universal recognition; and is often defined as a practice to increase the possibility of qualitative performance on a regular basis.
However, it can be best achieved when the performers are provided with a supportive and motivating team, along with some affirmative/ constructive interactions with the teammates.
The audit quality is maintained when it is capable of recognizing potential shortcomings/errors. The basic-yet-major issue concerned with audit analysis is the monetary loss (or risk for a loss) associated with the audit management system.
The audit quality is believed to thrive forever as one of the basic requirements for conducting an audit.
This, in turn, can be achieved if the auditors are prepared with relevant technical, technological, professional, and healthy skepticism and relevant experience.
Since it has not taken the actual shape for its future technological reference, it is assumed that the combination of data analytics with computer computing can take place soon.
And, that is when, we can encounter more accurate risk assessment tasks, setting benchmarks for identifying oddities for future references.


